Physicists have been searching for the mysterious dark matter for many decades. As
early as the 1930s, astronomers had been puzzled by a strange finding: galaxies held together even
though they should actually fly apart. In addition to the visible celestial objects – stars, planets and
clouds of gas and dust – there must therefore be some kind of invisible matter whose gravity keeps the
galaxies in check. But what is this ominous dark matter, without which it’s almost impossible to explain
how galaxies and galaxy clusters formed as the universe developed? Could it consist of still undetected,
ultralight or extremely heavy elementary particles? And are black holes related to this phenomenon?
Around the world, the search is on, and a new generation of experiments might soon be able to finally
solve the mystery of dark matter.
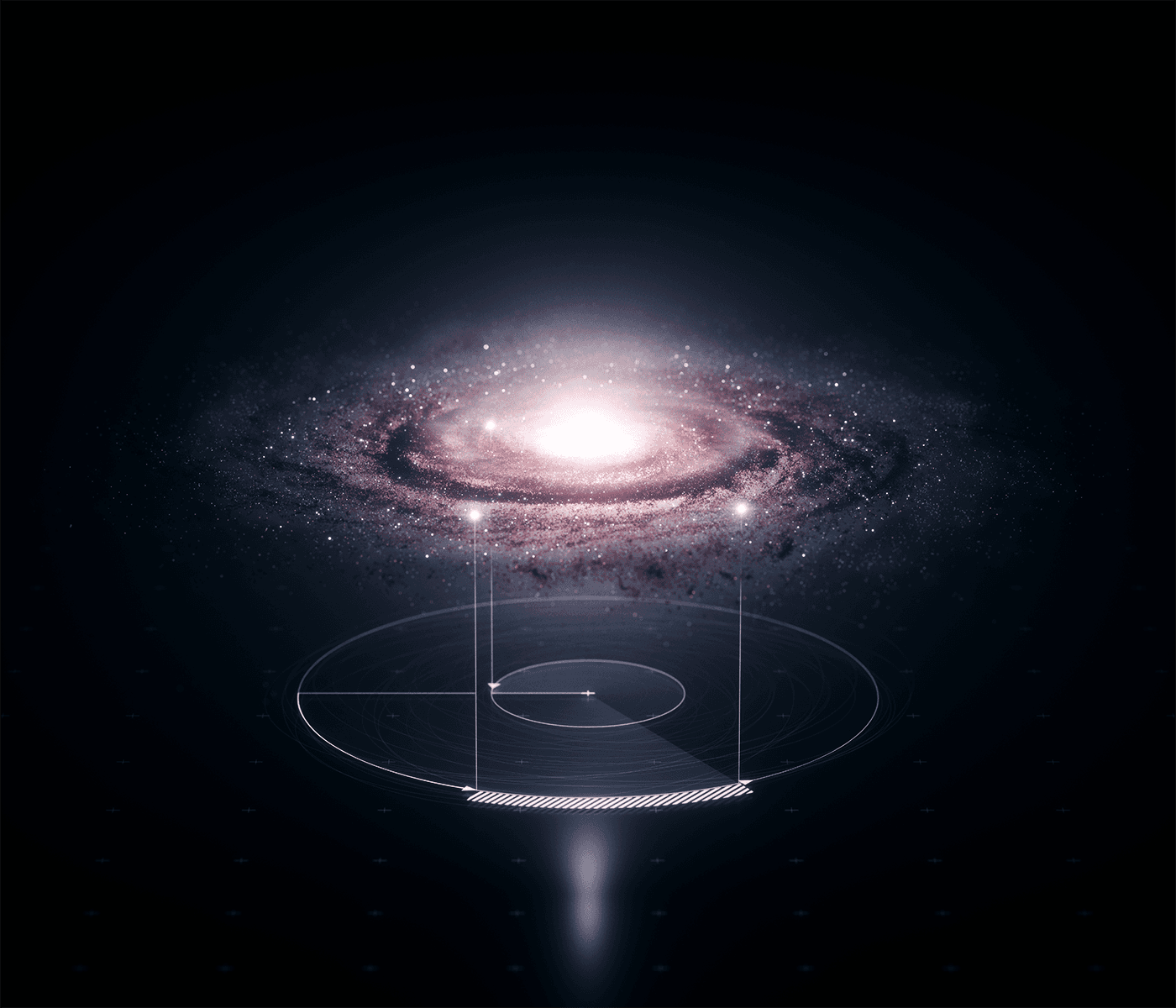
Rotation speed
In the 1970s, researchers observed that stars in the outskirts of a galaxy orbit
so fast that they should actually be catapulted out if the galaxy's gravity is coming only from the
visible matter. Their conclusion was that some kind of invisible, "dark" matter must be holding the
stars in their orbits with its extra gravity. This has prevented our Milky Way, for example, from
drifting apart long ago.

The strangest substance in the universe: dark matter is more than five times
more abundant in the cosmos than the matter we are familiar with. It does not interact with
electromagnetic radiation such as light and is thus completely invisible.
Temperature fluctuations
The cosmic microwave background radiation arose 380,000 years after the Big Bang
and is still billowing through the Universe. Small temperature fluctuations of the radiation such as those measured
by the European satellite “Planck” served as the seeds of future structures such as galaxy clusters.
The distribution of these tiny fluctuations indicate that dark matter already existed before any
galaxies formed.
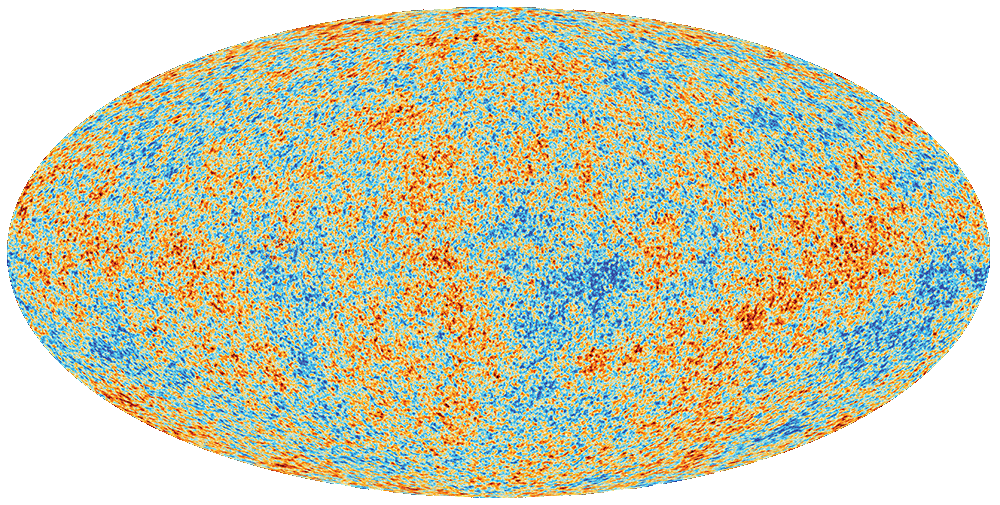
© ESA/Planck Collaboration
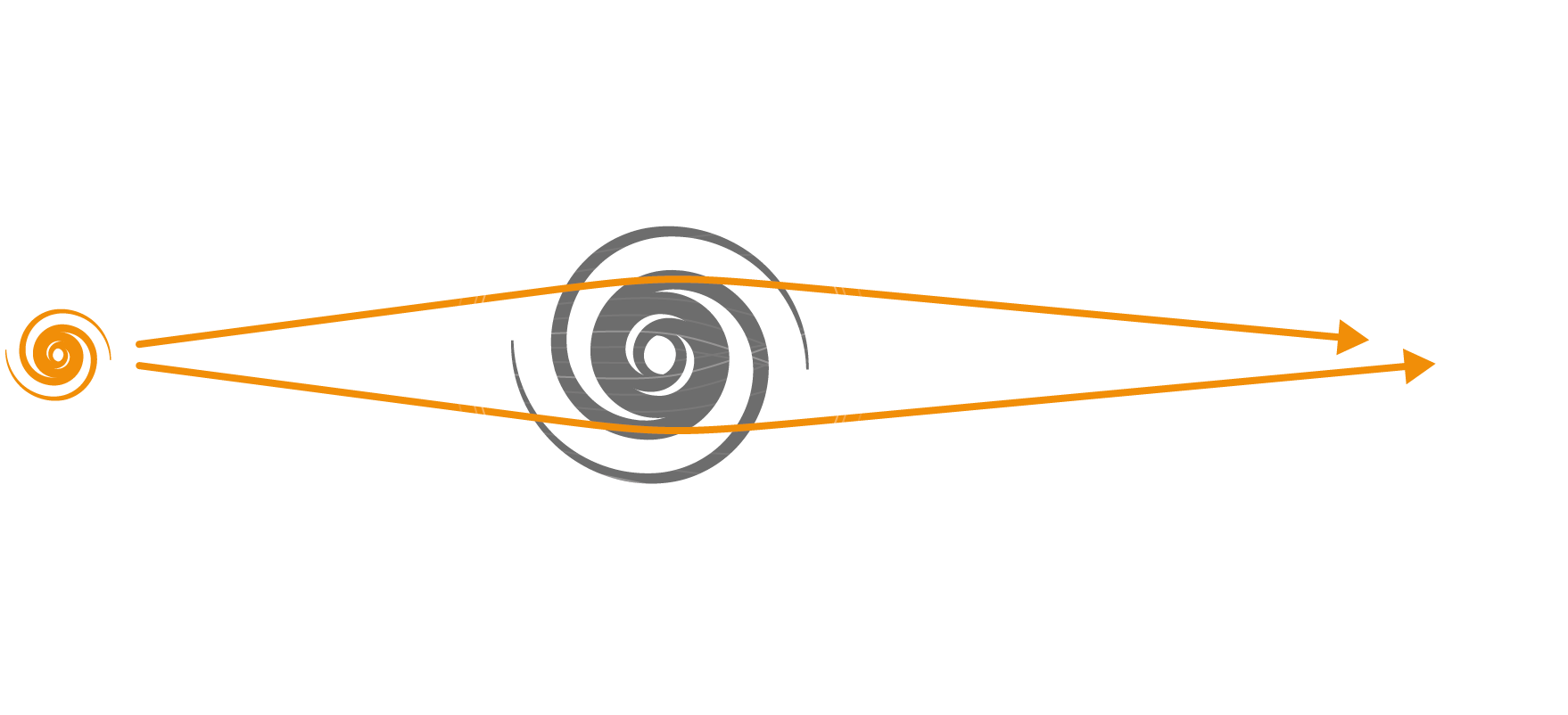
Gravitational lensing
Other evidence for the existence of dark matter is an effect called
gravitational lensing. Light from distant galaxies is deflected slightly because of dark matter‘s
gravitational pull.